May 29, 2024
When is Radiation Therapy a Part of Skin Cancer Treatment?
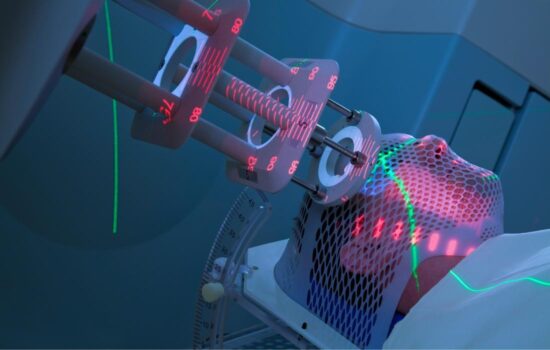
Radiation therapy may be part of skin cancer treatment when surgery is not an option, cancer is advanced, or there is a risk of recurrence. Consulting with an oncologist will determine whether and when radiation should be included in a treatment plan. Additionally, learn about possible side effects and tips for caring for your skin during radiation therapy.
Skin cancer occurs when skin cells begin to grow too fast. The most common cause is too much exposure to ultraviolet light. Over time, this can lead to changes to your skin, such as growths, new moles, or other changes in skin color. These abnormalities could develop into skin cancer.
Melanoma and non-melanoma are the two main types of skin cancer. Non-melanoma skin cancer is the most common type in the United States. While melanoma may be less common, it is more serious and tends to grow faster. The type of skin cancer you have will impact your treatment options. There are several different types of treatments for skin cancer depending on the type and where it’s located on your body.
Diagnosing Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is usually detected during a routine screening exam. This might be done by your primary care physician or a dermatologist. If you or your doctor find a suspicious spot that’s small, it can be entirely removed while in the office. If it’s larger, the doctor may take only a small amount to analyze the cells. This is called a biopsy. In either case, a pathologist will examine the cells removed to determine if cancer is present. The information provided in the pathology report will help your doctor decide which steps to take next.
Surgery, Radiation, and Other Skin Cancer Treatments
For most patients, surgery to remove the cancerous skin cells is the first step in the treatment process. In some instances, surgery is not possible, or the cancer has grown large enough that additional treatments are needed.
If the dermatologist feels that you would benefit from additional treatments, it’s best to consult with an oncologist. This type of doctor specializes in cancer treatment. The recommended treatment plan for skin cancer after surgery varies based on whether it’s melanoma or non-melanoma, and the stage of skin cancer. The location of the cancer on your body also plays a role in the treatment planning process. A plastic surgeon may be needed if it’s grown deep into the skin or if the cancer is located on the face or head.
For skin cancer that’s grown deep, has spread out to a larger area, or affected the lymph nodes, surgery may be followed by other treatments such as:
Radiation therapy: external beam or high-dose brachytherapy placed on top of the skin
Chemotherapy: These drugs are applied directly to the skin or via IV.
Immunotherapy: This therapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight the cancer cells
Targeted therapy: These drugs slow the growth of cancer cells by targeting a specific mutated gene.
When is Radiation Therapy Recommended for Skin Cancer?
External beam radiation therapy is delivered to the exact treatment area from a machine called a linear accelerator. Patients typically receive radiation treatments five days a week for three to eight weeks. It can be used for both melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers.
Here are some situations in which your oncologist may recommend radiation therapy as part of your skin cancer treatment plan:
If you have non-melanoma skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, surgery is typically the main treatment. However, your doctor may consider radiation therapy if surgery is not possible due to the size and location of the tumor or your health.
Your doctor may recommend radiation therapy after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. This reduces the risk of the cancer returning.
Radiation combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapy can make your treatment more effective. This is especially true for advanced or aggressive skin cancers.
If your skin cancer has spread (metastasized) to other parts of your body, radiation therapy can be used to shrink tumors so that pain and other symptoms can be reduced.
Does Radiation Therapy Have Side Effects?
Radiation therapy is intended to destroy cancer cells, but it can sometimes affect some healthy tissue in the area, leading to side effects.
The most common side effect of radiation is skin irritation similar to a severe sunburn. This usually improves after treatment ends. You may also feel tired or lose hair in the area of treatment. Talk to your radiation therapy team to understand possible side effects and how to treat them.
Caring for Your Skin During Radiation Therapy
You should protect your skin during radiation therapy. Here are a few quick tips:
Moisturize: To keep your skin hydrated, apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to the area at least twice a day.
Avoid irritants: Don’t use products with harsh chemicals, fragrances, or alcohol. These can increase sensitivity and irritation.
Guard against the sun: Wear loose clothing, hats, or sunscreen with a high SPF to protect the treated area from direct sunlight.
Handle with care: Be gentle when washing the treated area. Use lukewarm water and a mild, non-abrasive cleanser. Pat dry instead of rubbing.
Stay hydrated: Drink a lot of water to help your skin heal. This will also help maintain overall skin health.
Eat a balanced diet: Consume a nutrient-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to promote overall skin health and healing.
Relax: Practice relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, which can help reduce anxiety and promote skin healing during radiation therapy.
Find a Skin Cancer Doctor in Brevard County
If your skin cancer requires more than surgery, it’s a good idea to meet with an oncologist. The specialists at Cancer Care Centers of Brevard will work with you to create a personalized treatment plan. We are also available to provide a second opinion. We have offices throughout Brevard County Florida, including Melbourne, Merritt Island, Rockledge, and Palm Bay.
Categories: Skin Cancer, Radiation Therapy